PRTG Manual: Add a Group
Note: This documentation refers to the PRTG System Administrator user accessing the Ajax interface on a master node. For other user accounts, interfaces, or nodes, not all of the options might be available as described. When using a cluster installation, failover nodes are read-only by default.
In order to add a group manually, select Devices | Add Group from the main menu. An assistant will appear, leading you through two steps. For faster setup, you can select Add Group... in the context menu of a probe or group to which you want to add the new group. This will skip step 1 and lead you directly to step 2.
- Step 1
Please choose a probe or group you want to add the new group to. Click on Continue.
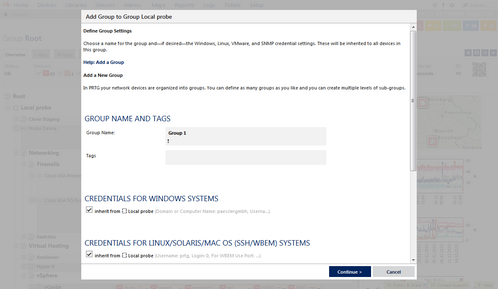
Add Group Assistant Step 2
- Step 2
Add group settings as described below.
Group Name and Tags |
|
|---|---|
Group Name |
Enter a meaningful name to identify the group. The name will be shown by default in the devices tree and in all alarms. |
Tags |
Enter one or more tags; confirm each tag by hitting the space, comma, or enter key. You can use tags to group objects and use tag-filtered views later on. Tags are not case sensitive. Tags are automatically inherited. |
Credentials for Windows Systems |
|
|---|---|
Domain or Computer Name |
Define the authority for Windows access. This is used for Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and other Windows sensors. If you want to use a Windows local user account on the target device, please enter the computer name here. If you want to use a Windows domain user account (recommended), please enter the (Active Directory) domain name here. If not explicitly defined, PRTG will automatically add a prefix in order to use the NT LAN Manager (NTLM) protocol. Please do not leave this field empty. |
Username |
Enter the username for Windows access. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
Password |
Enter the password for Windows access. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
Credentials for Linux/Solaris/Mac OS (SSH/WBEM) Systems |
|
|---|---|
Username |
Enter a login name for the access via SSH and WBEM. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
Login |
Define which authentication method will be used for login. Choose between:
|
Password |
This field is only visible if password login is selected above. Enter a password for the Linux access via SSH and WBEM. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
Private Key |
This field is only visible if private key login is selected above. Paste a private key into the field (OpenSSH format, unencrypted). Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. Note: If you do not insert a private key for the first time, but change the private key, you need to restart your PRTG core server service in order for the private key change to take effect! For details, please see Monitoring via SSH. |
For WBEM Use Protocol |
Define the protocol that will be used for WBEM. This setting is only relevant when using WBEM sensors. Choose between:
|
For WBEM Use Port |
Define the port that will be used for WBEM. This setting is only relevant when using WBEM sensors. Choose between:
|
WBEM Port |
This setting is only visible if manual port selection is enabled above. Enter the WBEM port number. |
SSH Port |
Define the port number which will be used for SSH connections. Note: By default, this setting is automatically used for all SSH sensors, unless you define a different port number in the sensor settings. |
SSH Rights Elevation |
Define with which rights the command will be executed on the target system. Choose between:
|
Target Username |
This field is only visible if sudo or su is enabled above. Enter a username to run the specified command as another user than root. If you leave this field empty, the command will be run as root. Ensure that you set the Linux password even you use a public/private key for authentication. This is not necessary if the user is allowed to execute the command without a password. |
Password Target User |
This field is only visible if su is enabled above. Enter the password for the specified target user. |
Credentials for VMware/XenServer |
|
|---|---|
User |
Enter a login name for access to VMware and XEN servers. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
Password |
Enter a password for access to VMware and XEN servers. Usually, you will use credentials with administrator privileges. |
VMware Protocol |
Define the protocol used for the connection to VMware and XenServer. Choose between:
|
Credentials for SNMP Devices |
|
|---|---|
SNMP Version |
Select the SNMP version that will be used for device connection. Choose between:
Note for SNMP v3: Due to internal limitations you can only monitor a limited number of sensors per second using SNMP v3. The limit is somewhere between 1 and 50 sensors per second (depending on the SNMP latency of your network). This means that using an interval of 60 seconds you are limited to between 60 and 3000 SNMP v3 sensors for each probe. If you experience an increased "Interval Delay" or "Open Requests" reading of the probe health sensor, you need to distribute the load over multiple probes. SNMP v1 and v2 do not have this limitation. |
Community String |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v1 or v2c are enabled above. Enter the community string of your devices. This is a kind of "clear-text password" used for simple authentication. We recommend using the default value. |
Authentication Type |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Choose between:
The chosen type has to match the authentication type of your device. Note: If you do not want to use authentication, but you need SNMP v3, for example, because your device requires context, you can leave the field password empty. In this case, SNMP_SEC_LEVEL_NOAUTH will be used and authentication will be deactivated entirely. |
User |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Enter a username for secure authentication. This value has to match the username of your device. |
Password |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Enter a password for secure authentication. This value has to match the password of your device. |
Encryption Type |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Select an encryption type. Choose between:
The chosen type has to match the encryption type of your device. |
Data Encryption Key |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Enter an encryption key here. If you provide a key in this field, SNMP data packets will be encrypted using the encryption algorithm selected above, providing increased security. The provided key here has to match the encryption key of your device. Note: If the key entered in this field does not match the key configured in the target SNMP device, you will not get an error message! Please enter a string or leave the field empty. |
Context Name |
This setting is only visible if SNMP version v3 is enabled above. Enter a context name only if it is required by the configuration of the device. Context is a collection of management information accessible by an SNMP device. Please enter a string. |
SNMP Port |
Enter the port used for SNMP communication. We recommend using the default value. |
SNMP Timeout (sec.) |
Enter a timeout in seconds for the request. If the reply takes longer than this value the request is aborted and an error message is triggered. |
Access Rights |
|
User Group Access |
Define which user group(s) will have access to the object you're editing. A table with user groups and right is shown; it contains all user groups from your setup. For each user group you can choose from the following access rights:
You can create new user groups in the System Administration—User Groups settings. |
Click on the Continue button to store your settings. If you change tabs or use the main menu, all changes to the settings will be lost!
Ajax Web Interface—Device and Sensor Setup—Topics
Other Ajax Web Interface Sections
Related Topics |
|---|
Keywords: Add,Add Group,Group,Group add